Necrotizing Fasciitis (Flesh Eating Disease) – Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment
What is Necrotizing Fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is described as a rare illness with severely damaging effects to the deep tissue and skin layers, it is a very swift spreading infection of the soft tissues and connectives tissues that cause the affected areas to just waste away and undergo tissue necrosis. Any part of the body may be affected by this condition and has no particular risk factors. Studies on the occurrence of this disease have found out that the most common pathogen causing necrotizing fasciitis is a particular species of bacteria under the so called, group A beta hemolytic streptococci, which is the streptococcus pyogenes,anf for some time, this was the only recognized causative agent of this particular condition. But recent studies have completely shattered this notion, because now we know that a host of other microorganisms can cause this debilitating sickness, such as other bacteria and some species of fungi. Bacteria are the most common pathogens bringing about this condition and some of the bacterial toxins also have the ability to activate the T-cells or T lymphocytes of the body, releasing excessive amounts of immune modulating substances called cytokines and causing a condition called toxic shock syndrome.
Although the disease might have been present since the earliest days of our ancestors, it was not until the middle 1800s that physicians started to describe this condition, there were lots of other names for it then but in 1952, it was officially named necrotizing fasciitis. This disease has also been called “flesh-eating bacterial infection” or simply, “flesh eating disease” among other things, because the progress of the condition through the tissues is so fast that you would believe that the skin is being eaten right before your eyes. But as opposed to the “flesh eating bacterial disease” notion, the bacteria do not actually eat the tissues, they release a variety of substances and toxins that “dissolve” the soft tissues and skin, causing necrosis at an extremely fast rate Any infection with this disease is treated as an ongoing emergency situation, therefore, a quick and effective response is imperative to the survival of the patient.
Necrotizing Fasciitis Causes
It was first thought that group A beta hemolytic streptococci were the only organisms able to cause necrotizing fasciitis but as more studies were done on a variety of cases, it has been found out that a variety of other organisms can cause the condition.
The causative microorganisms were found out through the different tissue cultures that were done from cases of necrotizing fasciitis and it was found out that more often than not, different strains of bacteria and other microorganisms are found on the tissue, leading to the theory that these microorganisms are inadvertently working together and complimenting each other’s virulence factors, also called coninfection. For example, one type of aerobic bacteria can cause tissue destruction on the upper layers of the skin, another strain releases toxins to stop the immune cells’ functions and cause tissue destruction or necrosis, the resulting necrotic tissue on the deeper layers become anoxic or without oxygen, this is where opportunistic anaerobic bacteria move in and multiply, releasing even more toxic substances to eat away at the different connective tissues.
Some of the most common microorganisms found in cultures of necrotizing fasciitis patients are;
- S. pyogenes
- Group A Streptococci
- Group A Staphylococci
- Clostridium spp
- Peptostreptococcus
- Klebsiella
- E. Coli
- Pseudomonas
- Vibrio vulnificus.
Necrotizing Fasciitis Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis include a variety of visible skin conditions but the disease often begins with cases of immunosuppresion, an existing infection, or an open lesion or wound. Immunosuppressive cases include unregulated drug use, alcoholism, diabetes, and other chronic systemic diseases, once the immune system is compromised by these conditions, necrotizing fasciitis causing micro fauna are able to establish themselves in the tissue before the immune system can detect and counteract them.
Some of the symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis are:
- Delayed healing with the lesions becoming tender, swollen, and reddened.
- Diarrhea
- Nausea, and vomiting coupled with fever and chills,
- Increased redness in the affected area
- Flaking of skin
- Blisters or bullae
- Darkening of the skin from pinkish to red, to dark red and violet
- Black areas of necrotic tissue or eschars become apparent
- Leaking fluid from the deeper parts of the skin
- Gas formation in the tissues giving off a pungent and foul odor
- Septic infection
Three subtypes of the disease causes include;
- Type 1 – the condition stems from supposedly “sterile” means of trauma like surgical wounds
- Type 2 – skin trauma is simple and small like insect bites, abrasions, and small cutes
- Type 3 – skin trauma is more extensive and the wounds come in contact with things harboring the causative organisms themselves, this is the type with the fastest progress of the disease and gangrene or tissue death often occur within a few days.
Necrotizing Fasciitis Pictures
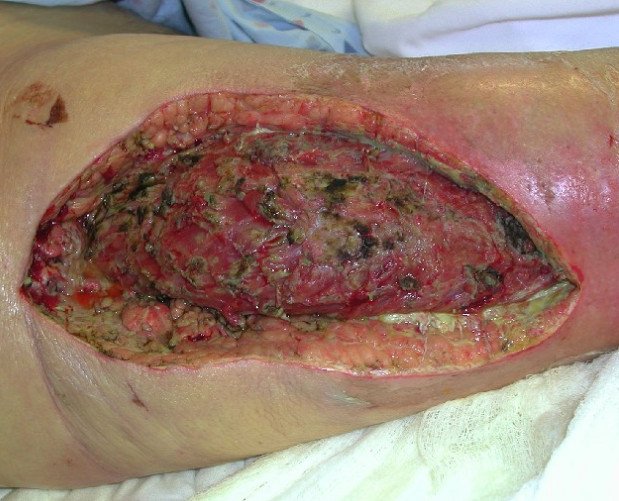
Picture 1 : Necrotizing Fasciitis photo
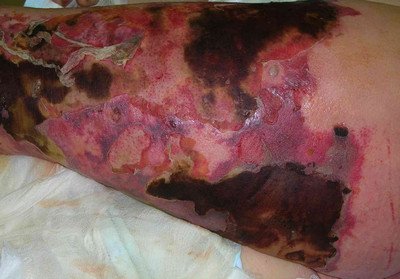
Picture 2 : Necrotizing Fasciitis on leg
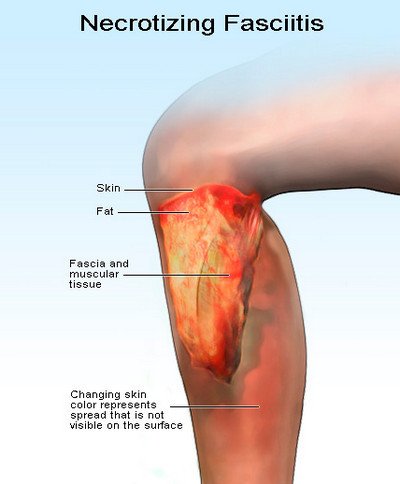
Picture 3: Necrotizing Fasciitis (diagram)
Image source: MedicineNet
Necrotizing Fasciitis Statistics
Because this disease spreads so fast within the body yet so rare in terms of occurrence, varying statistics are available about it. It is generally known that more than 1000 people are affected each year, with the numbers rising slightly every year, and more than 20 percent of these cases become mortalities even with complete access to treatment. 70 percent have predisposing immunosuppressive conditions and there is a more than 70 percent mortality rate for cases with little or no access to treatment.
Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment
Because this disease progresses at a terrifying speed, all cases are treated as emergency situations, and early antibiotic treatment is often employed to try and slow the progress of the disease. Both intravenous and oral antibiotics with wide spectrums are employed to counteract the disease progress, and once the exact microorganisms are determined through tissue cultures, more specific acting antibiotics are given to the patient. Surgery is often an unavoidable part of the treatment in order to halt the spread of the infection, debridement, or manual removal of dead and infected tissue is often done on the lesions of patients to determine the extent of the disease. Amputation is often necessary to save the healthy tissue and make sure that the infection does not reach other parts of the body, and the wound is closely monitored for signs of reappearing infection.