What is Toenail fungus?
Naturally, nails assist a person to control objects, help in a person’s sense of touch and protect the underlying tissues. When a nail is infected with fungus, nails become very hideous; which prompts a person to undergo treatment.
As the name suggests, toenail fungus refers to a nail infection which is fungal in origin. The disease is also known by different designations, such as dermatophytic onychomycosis and tinea unguium. This is considered as the most frequent nail disease which represents roughly ½ of all irregularities concerning the nails.
The problem is not only limited to toenails, though remarkably infrequent, it can also crop up in the nails of the fingers. Infrequently, children are affected. Its occurrence in the adult population is around 5 to 10 percent, yet anyone can have toenail fungus especially when nails are damaged and microscopically fissured, permitting fungal spores to initiate an infection. Diabetic patients are more vulnerable, the same as those who are immunocompromised.
Risk factors which both support and promote fungal infection include advancing age, poor personal hygiene, warm climate, constrictive shoes which keep the toes moist, physical activities which cause constant trivial injury to the hyponychium, walking barefoot in public and shared places and chronic diseases affecting the circulation and immune system.
Classification
Toenail fungus can be classified into 4 characteristic types, namely distal subungual onychomycosis, white superficial onychomycosis, proximal subungual onychomycosis and candidal onychomycosis.
- Among the four classic forms, the distal subungual onychomycosis which is typically attributable to Trichophyton rubrum infection is the most frequent form of toenail fungus. In this condition, there is involvement of the nail bed, as well as the base of the nail plate.
- The second type comprises for about 10 % of toenail fungus. In white superficial onychomycosis, the fungi invade the external layers of the nail plate, resulting to the formation of white spots on the plate.
- The least familiar type of toenail fungus is proximal subungual onychomycosis. This type is characterized by fungal infiltration of the recently formed nail plates via the proximal nail folds. Mostly affected individuals are those with weakened immunity.
- In the case of candidal onychomycosis, a previously damaged nail which is repeatedly submerged in water becomes infected by Candida.
Symptoms
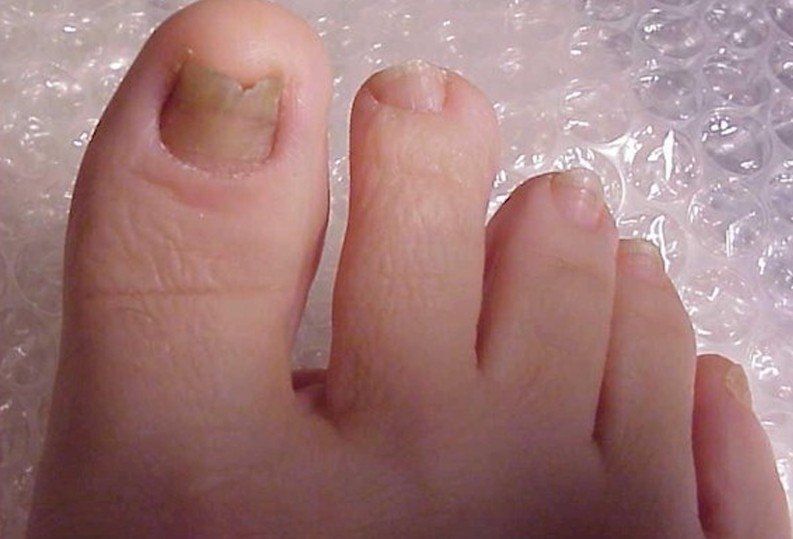
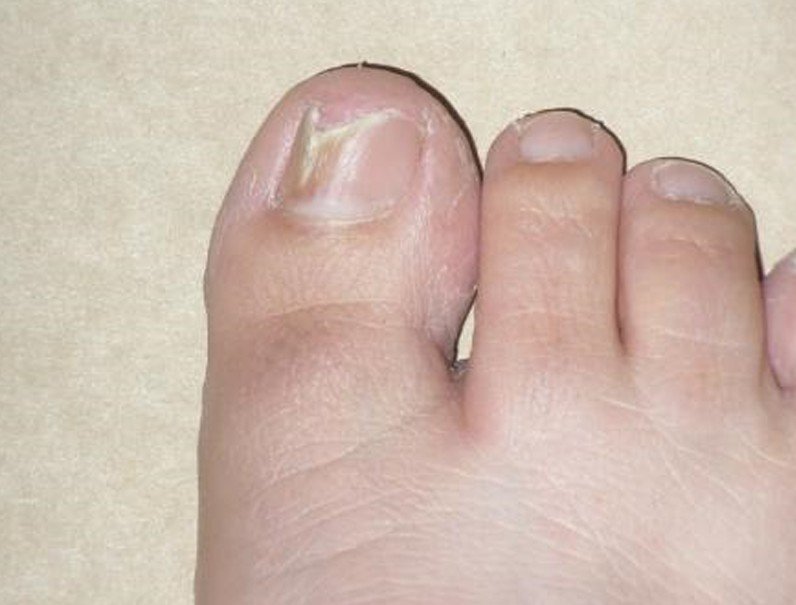
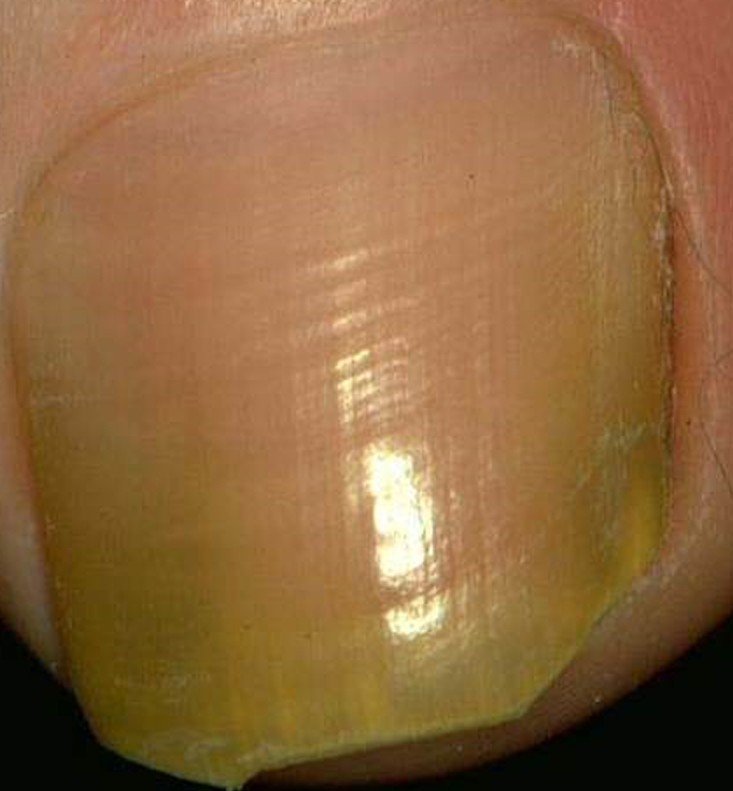
- The nail plates become thickened, yellow brown in color and dull. Changes in its molecular components make the nails coarse and brittle leading to disfigurement, and may easily break away from the nail beds.
- The change in the nail’s appearance regularly begins at the end of the nail or the hyponychium before affecting the whole nail. Still, pattern of nail changes may vary depending on what type of toenail fungus a person has. In a process known as onycholysis, the nail plate partially separates from its bed. Further separation results when the ends turn yellow and fragments of keratin forms beneath the nail. From this debris grow the fungus which causes the nails to turn weak and brittle.
- Most likely to be affected are the big and little toes.
- Foul smelling substance is noted under the nails.
- Patients may not feel any pain or other physical indications, except for severe cases.
- Not only does it cause a cosmetic problem, since a disfigured nail restricts a person’s normal activities. Contained in the footwear, the nails might be compressed resulting to pain and tenderness. Walking becomes difficult and diminished mobility can be noticed.
- Dermatophytids describe cutaneous lesions that occasionally come out as an effect of a fungal infection.
- Affected people may also go through major psychosocial issues related to the appearance of the toenails.
Treatment
Treating fungal nail infections are frequently challenging given that the root of infection is implanted within the nail making it hard to get access and also, complete healing may take several months under antifungal drugs.
- Clean the feet everyday with mild soap and water, dry meticulously and apply prescribed foot powder. Nails must be well-trimmed. Avoid the use of nail polish.
- When infection only affects the nail ends, topical antifungal creams can be applied on the affected toenail although it may not make its way into the nail plate to completely cure the infection. Certain medications such as ciclopiroxolamine and butenafine are found to be successful however these drugs must be utilized each day for at least one year.
- Systemic antifungal medications like itraconazole and terbinafine can also be prescribed in conjunction with topical creams to effectively break in the nail bed. Even the infection has already disappeared, treatment is still continued to avoid re-infection.
- When immobility due to pain becomes a problem, surgery to remove the abnormal nail is necessary to cure the problem successfully. Surgical tactics consist of nail avulsion and matrixectomy.
Home Remedies
Like any other medical conditions, there are several alternative medicines which are used by many, albeit the unverified effectiveness.
- Tea Tree Oil
- This is a strong antiseptic and fungicide. On a daily basis, the affected nail is directly applied with unadulterated tea tree oil.
- Solution of warm water and natural apple cider vinegar
- In this remedy, the diseased toenails must be submerged in a basin with equal concentration of warm water and vinegar for about fifteen to twenty minutes.
- Oregano and olive oil
- Oregano oil is found to be an effective home remedy as this has some antiseptic, antifungal and analgesic effects. Mix two drips of Oregano oil and one teaspoon of the latter. The mixture must be directly spread over the affected nail for less than 3 weeks.
- Grape fruit seed extract
- Snakeroot
- Listerine Mouthwash with undiluted lemon juice
- Mouthwash can also be a good alternative treatment given that mouthwash has salicylate thymol and euchalyptol. Commonly, this form of treatment requires the addition of a natural acid such as pure lemon juice. With the addition of a natural acid, the fungal growth will be certainly hindered, therefore, preventing infection from further spreading. The procedure is simple. An adequate amount of mouthwash is mixed with the same amount of vinegar in a basin. The affected foot is immersed for at least twenty minutes once a day.
Laser Treatment
Lasers have now become broadly accepted in treating human conditions. These are nowadays becoming practical in medical and surgical care of various diseases, such as in nail fungus.
Laser therapies make use of a concentrated flash of energy which is, depending on what wavelength it has been set, capable to selectively break up particular anatomical organs that have become diseased, and plainly vaporize them.
In the early days, laser application in treating onychomycosis was only to form holes and pathways heading to nail’s underneath in a procedure known as fenestration. With these outlets, the infected area gains better access to topical medications. However, this method didn’t encounter with much success. So, an enhanced approach is implemented. At the moment, a Noveon-type laser is being used as this laser system has been found to be relatively effective.
In laser therapy, the physician will operate on a light source to be concentrated on the affected toe. The laser is aimed at the toenail and its matrix. It is effective in destroying the causative fungus and is comparatively painless as nails are just dead cells.
Toenail fungus Pictures
source : doctorsecrets.com
source : yolasite.com
source : yolasite.com
source : toenail-fungus-treatments.com
Toenail fungus Pictures
source : justprnews.com